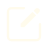
此处省去课堂上讲解的一维数组和多维数组(花式位置索引)等索引方法,此篇文章旨在补充布尔索引 boolean indexing知识点
以bool数组作为索引
bool数组可以通过直接指出保留的值(True)与舍弃的值(False),来构建输出的数组。
bool数组的shape需要与被索引的数组(的前若干个维度)shape严格对齐。
我们通过下面的例子来理解:
Selecting data from an array by boolean indexing always creates a copy of the data, even if the returned array is unchanged.
(通过布尔索引从一个数组中选择数据,总是创建一个数据的副本,即使返回的数组没有变化。)
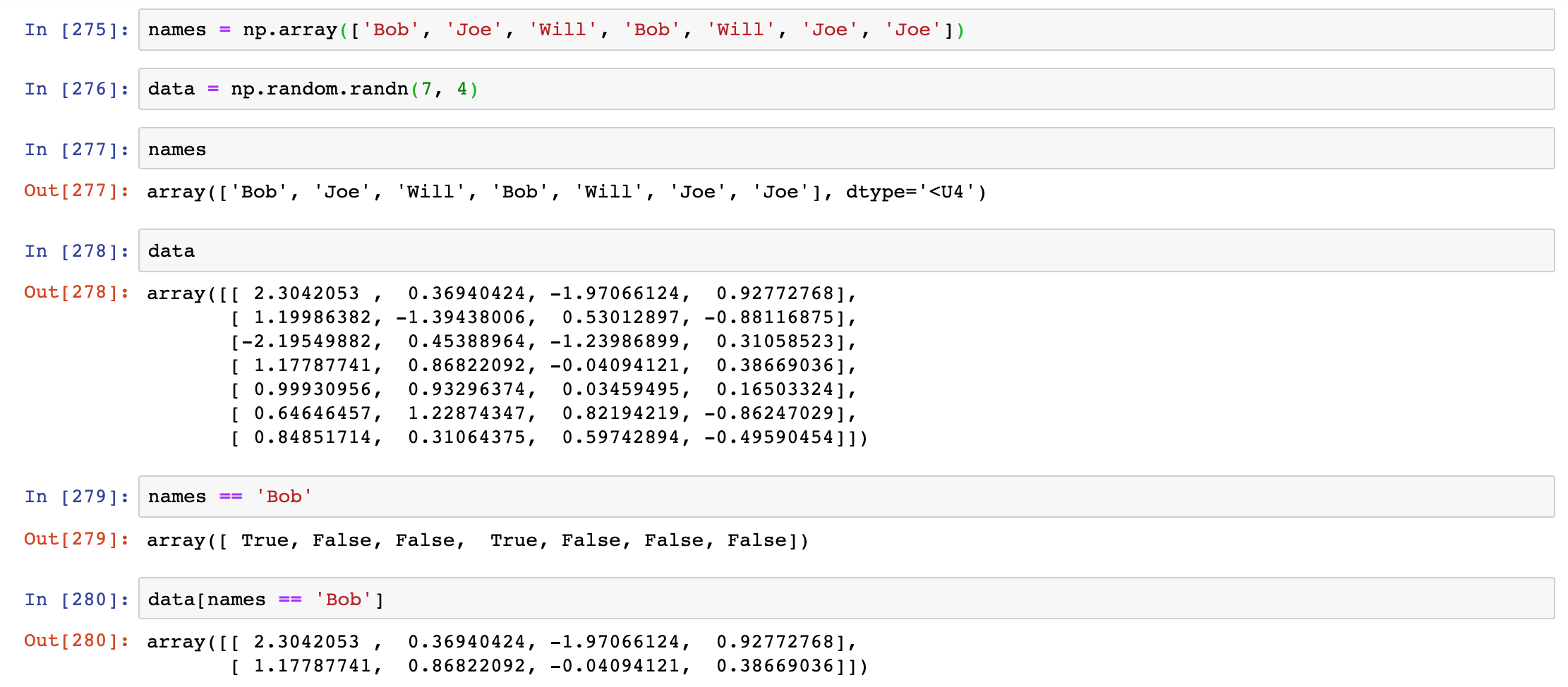
select from the rows where names == 'Bob' and index the columns
(从姓名=='Bob'的行中选择,并对该列进行索引)

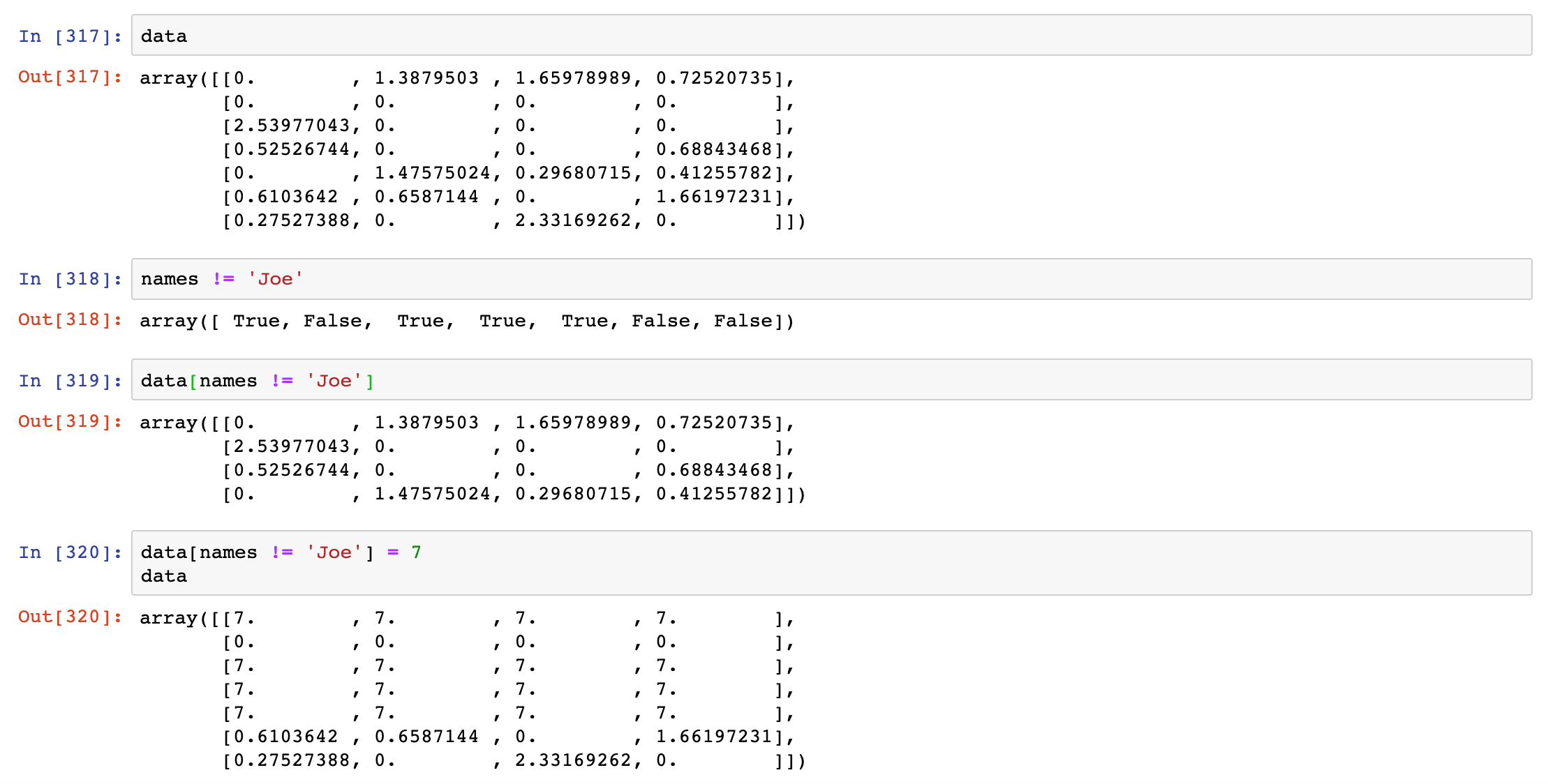
select everything but 'Bob', you can either use != or negate the condition using ~
(选择除'Bob'以外的所有内容,你可以使用!=或者使用~来否定条件。)
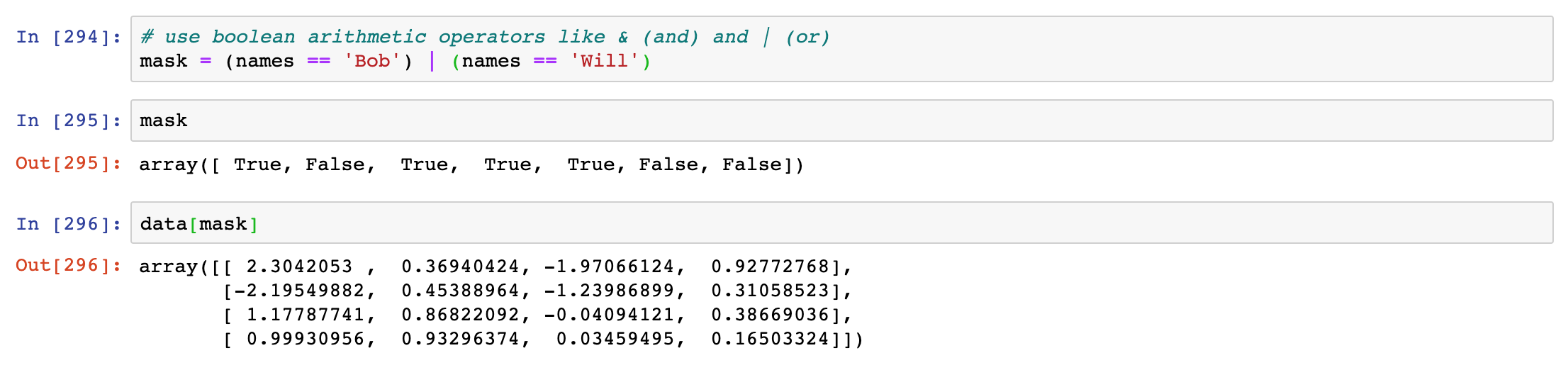
select two of the three names to combine multiple boolean conditions, use boolean arithmetic operators like & (and) and | (or)
(选择三个名字中的两个来组合多个布尔条件,使用布尔算术运算符,如&(和)和|(或))
Note: The Python keywords and and or do not work with boolean arrays. Use & (and) and | (or) instead.
(注意:Python的关键字and和or对布尔数组不起作用。请使用 & (和) 和 | (或) 来代替)
Setting values with boolean arrays works in a common-sense way. To set all of the negative values in data to 0 we need only do
(用布尔数组设置数值是以一种常识性的方式进行的。要把数据中所有的负值设置为0,我们只需要进行下面操作)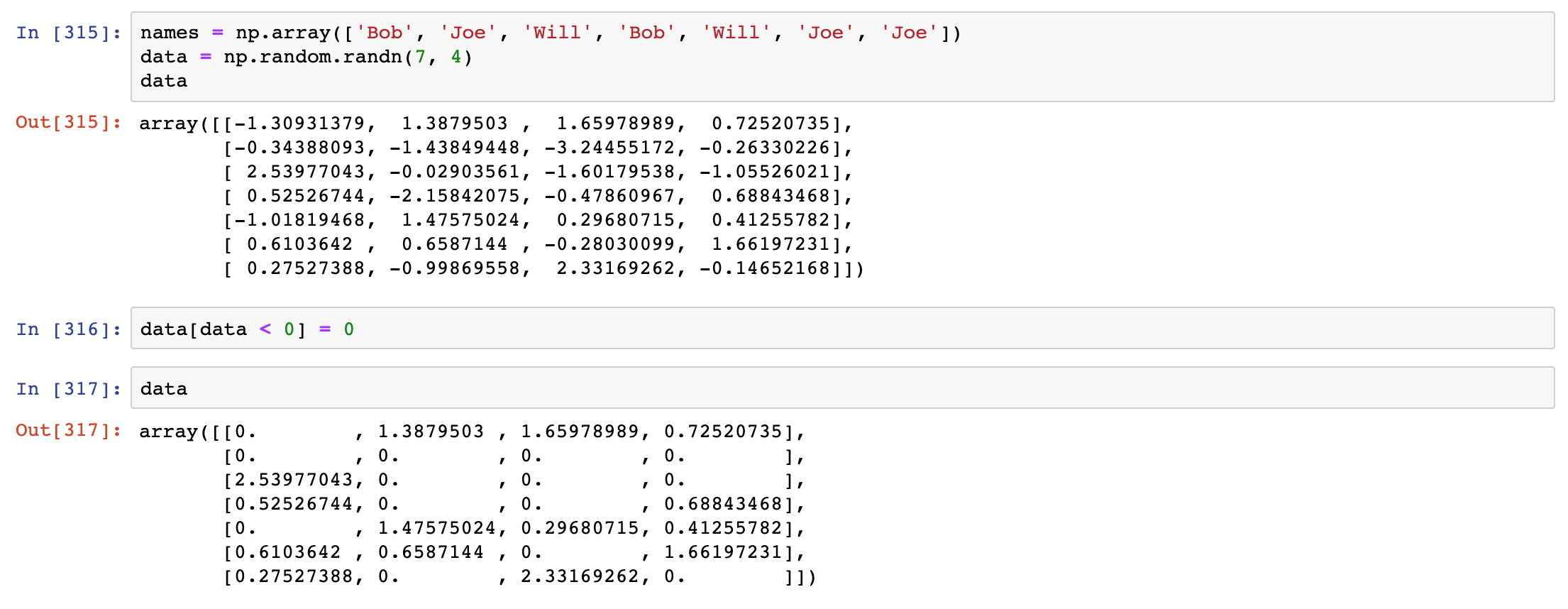
Setting whole rows or columns using a one-dimensional boolean array is also easy
(使用一维布尔数组设置整个行或列也很容易)
原文出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/agilestyle/p/12246045.html
 27.9983
27.9983
 4
4
 0
0

 关注作者
关注作者
 收藏
收藏
 发表评论
发表评论
暂无数据