python中日志logging模块的性能及多进程详解
使用Python来写后台任务时,时常需要使用输出日志来记录程序运行的状态,并在发生错误时将错误的详细信息保存下来,以别调试和分析。Python的logging模块就是这种情况下的好帮手。本文就介绍了python中日志logging模块性能及多进程的相关资料,需要的朋友可以参考下。
Java 中最通用的日志模块莫过于 Log4j 了,在 python 中,也自带了 logging 模块,该模块的用法其实和 Log4j 类似。日志是记录操作的一种好方式。但是日志,基本都是基于文件的,也就是要写到磁盘上的。这时候,磁盘将会成为一个性能瓶颈。对于普通的服务器硬盘(机械磁盘,非固态硬盘),Python日志的性能瓶颈是多少呢?今天我们就来测一下。下面话不多说,来一起看看详细的介绍:
测试代码如下:
结果为:
Start test ....
2973.0 rows per second
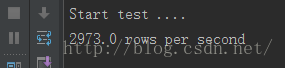
Python的logging性能:
7200转的机械磁盘,测了几次,每秒的能写入日志的行数(每行就是一条日志),数量基本在 2800-3000 之间。此时,磁盘IO基本已经跑满。(在3.3Ghz的CPU上,CPU占用大约40%)。
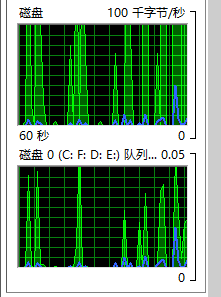
Python的logging多进程:
python 的 logging模块,是线程安全的。但对于多进程的程序来说,怎么去写日志文件呢?我的解决办法是,每个进程的PID,写一个单独的日志文件。再用算法把所有进程的日志合并起来,生成新的日志。
提示:由于磁盘IO已经到达瓶颈,所以多进程并不能提高日志性能。高性能日志,需要用缓存,或者分布式日志。
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作能带来一定的帮助.

数据分析咨询请扫描二维码